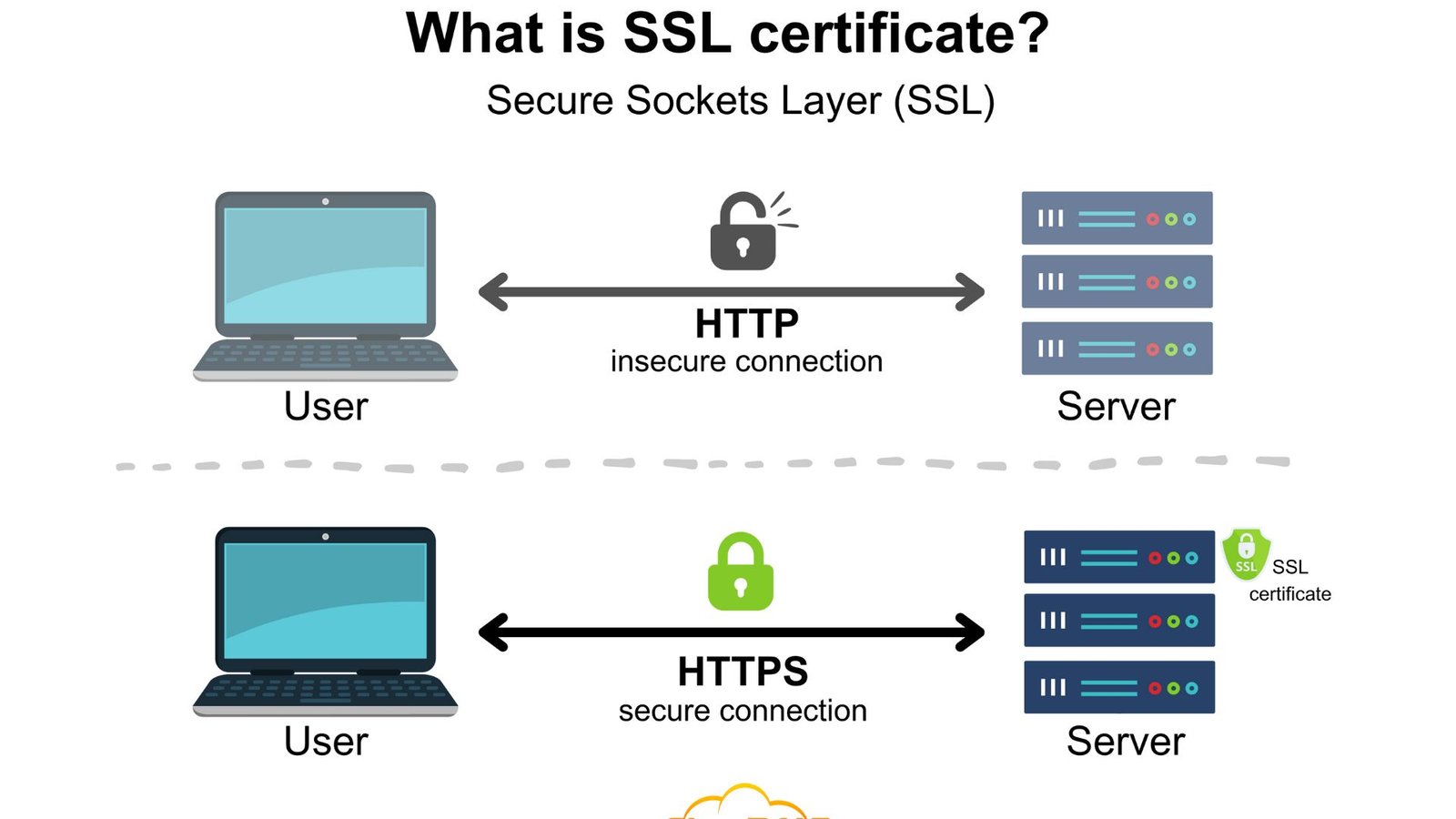
Implementing SSL certificates for enhanced security is crucial for protecting your website and its users. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates encrypt the data exchanged between your website and its visitors, ensuring a secure connection. Here’s a detailed guide on how to properly implement SSL certificates to boost your site’s security.
1. Understand the Benefits of SSL Certificates
Before you start, it’s essential to know why SSL certificates for enhanced security are important. SSL certificates encrypt data, such as login details and payment information, making it nearly impossible for hackers to intercept and read. Additionally, having SSL improves your website’s credibility and SEO rankings, as search engines prefer secure sites.
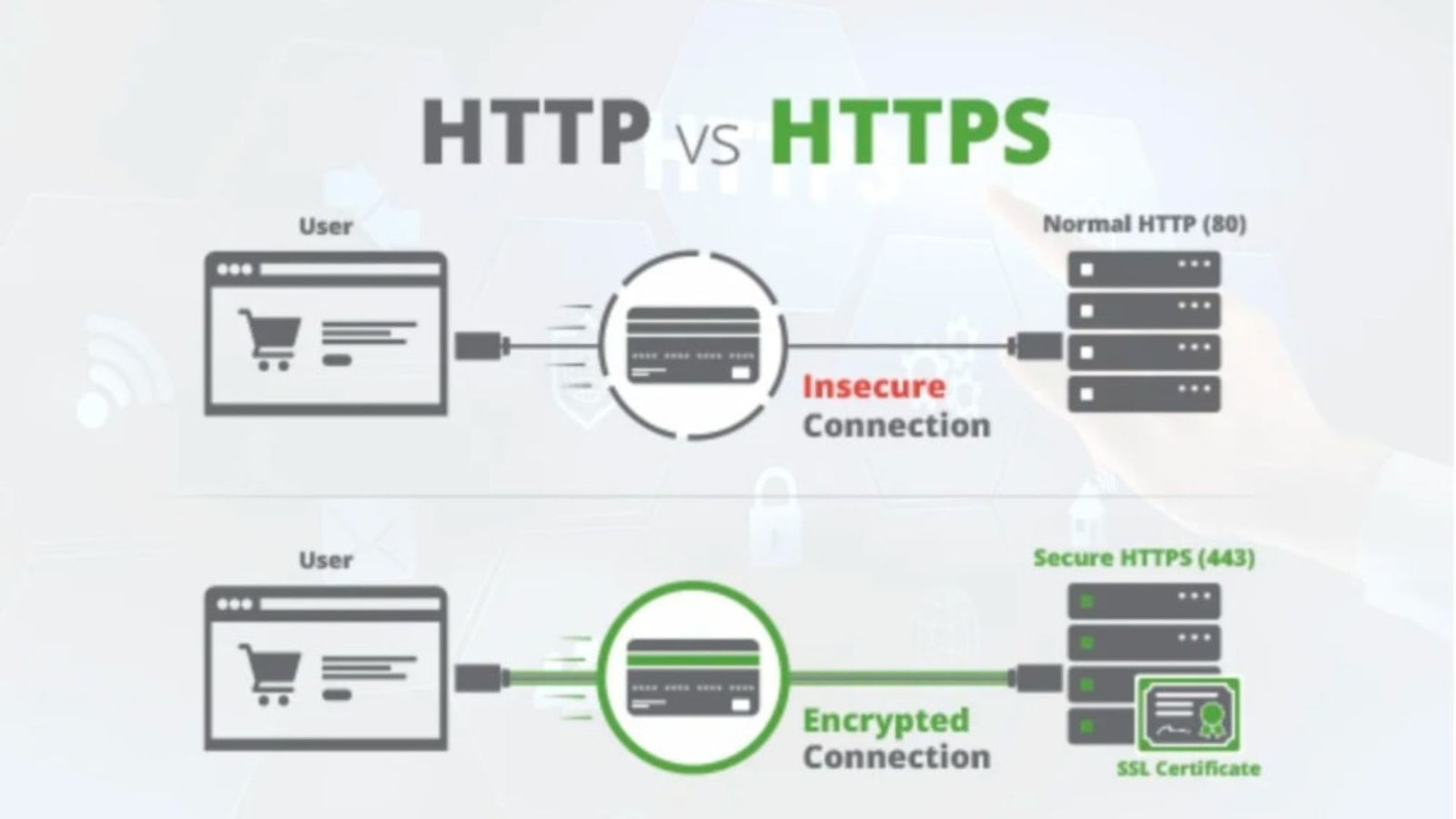
2. Choose the Right Type of SSL Certificate
There are several types of SSL certificates, each catering to different needs:
- Domain Validated (DV) SSL: Provides basic encryption and is suitable for small websites.
- Organization Validated (OV) SSL: Offers a higher level of security and verifies the organization’s identity.
- Extended Validation (EV) SSL: Provides the highest level of security and displays a green address bar, enhancing trust.
Choose the type that best fits your website’s requirements.
3. Purchase an SSL Certificate
To obtain an SSL certificate, you need to purchase it from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). Popular CA providers include Let’s Encrypt (which offers free certificates), DigiCert, and Comodo. When purchasing, ensure that the CA is reputable and provides adequate customer support.
4. Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
A Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is a block of encoded text that you need to generate on your web server. The CSR contains your website’s public key and is used by the CA to create your SSL certificate. Most hosting providers offer tools to generate a CSR easily.
5. Submit the CSR to the Certificate Authority
Once you’ve generated your CSR, submit it to your chosen CA. The CA will use the CSR to create your SSL certificate. Depending on the type of certificate you purchased, the CA might require additional documentation for validation.
6. Install the SSL Certificate on Your Server
After receiving your SSL certificate from the CA, you need to install it on your web server. The installation process can vary depending on your hosting provider and server type. Generally, you’ll need to upload the certificate files and configure your server to use them.
7. Update Your Website’s Links to HTTPS
After installing your SSL certificate, update all links on your website to use HTTPS instead of HTTP. This includes internal links, images, and resources. Updating these links ensures that visitors are redirected to the secure version of your site.
8. Configure Redirects for HTTP to HTTPS
Set up automatic redirects from HTTP to HTTPS to ensure that visitors who access your site via the old HTTP links are redirected to the secure HTTPS version. This helps maintain a secure connection and avoids potential security warnings for your visitors.
9. Check for Mixed Content Issues
Mixed content occurs when an HTTPS page contains resources (such as images or scripts) loaded over HTTP. This can cause security warnings and undermine the security of your site. Use tools like SSL Checker to identify and fix mixed content issues.
10. Test Your SSL Certificate Installation
Verify that your SSL certificate is installed correctly using tools like SSL Labs’ SSL Test. These tools will check your site’s SSL configuration and ensure that it meets industry standards for security.
11. Monitor Your SSL Certificate Expiry Date
SSL certificates have an expiration date, typically ranging from one to two years. Set up reminders to renew your certificate before it expires to avoid any disruption in your site’s security. Many CA providers offer automatic renewal options.
12. Enable HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) is a security feature that forces browsers to use HTTPS for all communications with your site. Enabling HSTS helps protect your site against certain types of attacks and ensures that visitors always use a secure connection.
13. Regularly Update Your SSL Certificates
Keep your SSL certificates updated to maintain strong security. Regularly review and renew your certificates to adapt to new security standards and avoid vulnerabilities.
14. Educate Your Team About SSL Security
Ensure that everyone involved in managing your website understands the importance of SSL and how to maintain it. Educating your team can help prevent security lapses and ensure that your site remains secure.
15. Address Any Security Warnings Promptly
If your site displays any security warnings related to SSL, address them immediately. Warnings can deter visitors and harm your site’s credibility. Regularly monitor your site’s security to detect and resolve any issues quickly.
Conclusion
Implementing SSL certificates for enhanced security is a crucial step in safeguarding your website and its users. By following these steps, from choosing the right type of certificate to ensuring proper installation and maintenance, you can provide a secure browsing experience and protect sensitive information. Embrace SSL to boost your site’s security and trustworthiness.